
The Ethereum Beacon chain is one of the few options for improving Ethereum. Thus, there is evidence of a chain of work. The process requires tons of processing power. Proof of work gives more rewards to people with better equipment and connectivity. This means that the higher your hash rate, the more likely it is to solve the puzzle first. Thus, the concept of proof of work is really wasteful, because only one miner receives a reward, and all the work of other miners is lost. To change this, we need to implement the concept of stake protection.
Ethereum Lighthouse
The existing concept of proof of work on the Ethereum blockchain will continue to exist. In parallel with our main blockchain, there is another blockchain. The so-called chain of lighthouses. Thus, there are smart contracts that work in the main chain. And as part of the main state of the network, an agreement will be concluded according to which users will be able to send deposit transactions. Thus, you have a second blockchain that works with the concept of proof of bet, but still depends on the main chain.
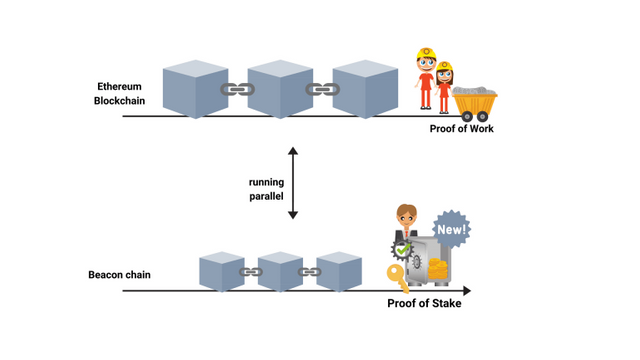
Ethereum lighthouse chain
What are the requirements for a beacon circuit?
Thus, you can send your 32 Ether to a deposit agreement along with two other parameters. Thus, the function has 3 parameters. First of all, any transaction that is deposited must contain 32 ethers. You also need a specific pub key and a specific withdrawal address. So you will have the pub key for Ethereum, and then you will have another pub key that you use for output.
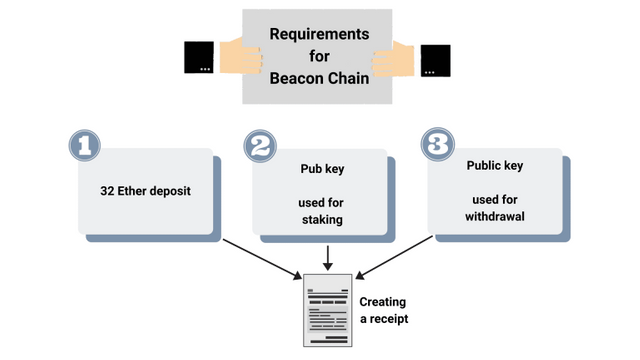
This way you are providing some data and at least you have two publication keys. When you enter the correct transaction, it creates a receipt. Thus, any client of a stake confirmation beacon chain will need at least sufficient access to a work proof chain. Therefore, you should know what block hashes are and what deposit receipts were between any two control points. Thus, to prove customer interest, it is enough to be an easy customer.
How does the lighthouse circuit work?
Thus, the lighthouse chain will exist parallel to the chain of Ethereum blocks. Due to the rating mechanism, it is likely to have a level much lower than 25 percent. Thus, some signs of cola blocks have pointers that point to the main chain. Later blocks of the lighthouse circuit indicate later blocks in the main circuit. Therefore, there is a strict rule of consensus.
Thus, the link to the main chain of the child element must be either the same or a descendant of the link to the main chain of the ancestor. When you process a later block, it will be part of the agreed rules, which you must also follow.
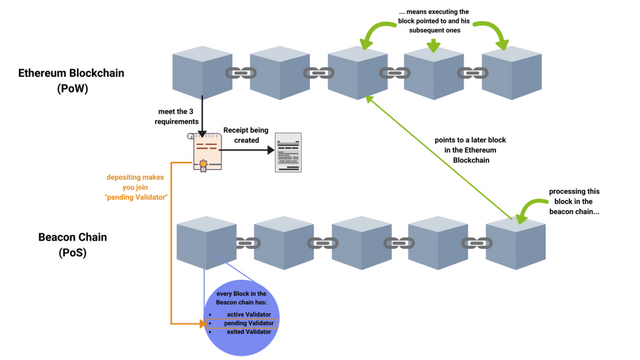
Thus, the one who made the deposit earlier will ultimately add himself to the waiting set of the validator, which is stored in a later block. Inside the beacon chain, you have several sets of validators. Thus, in the current set, you have an active validator, a pending validator and an installed validator. Thus, if you make a deposit, you will be combined into a pending validator set.
How does the lighthouse circuit work?
The lighthouse chain is located between the main chain and fragments. It is like connective tissue that provides a heartbeat. A smart contract for the current Ethereum blockchain will allow validators to participate in the protocol proving participation in the 32 Ether draw.
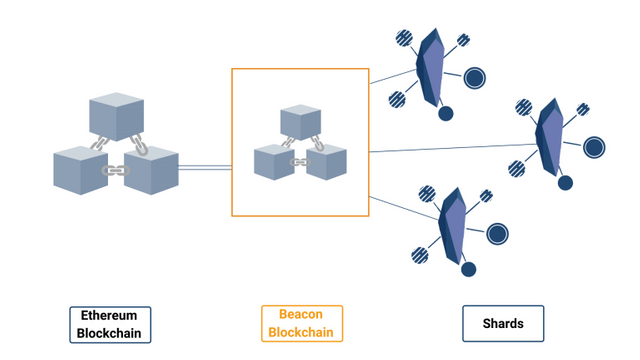
Once placed in a pending set of validators in the beacon chain, they can become active validators and can participate in the stake protection protocol.
The beacon chain then generates a random number for randomly selecting validators to propose a block and voting responsibilities. With this random sampling, we stop the collusion between validators and the impact on the system.
The Ethereum Lighthouse circuit is summarized:
The Ethereum lighthouse chain runs parallel to the Ethereum blockchain.
The lighthouse network is based on the concept of proof of stake
If you want to participate in the betting verification protocol, you need 32 Ether, a pub key and an address for withdrawing funds.
There are pointers in the proof of the bet blocks that point to the main chain.
The one who made the deposit earlier adds himself to the validator waiting set, which is stored in a later block.
Detailed information:
Website: https://ethereum-beacon.com/
White Paper: https://ethereum-beacon.com/whitepaper.pdf
Twitter: https: // twitter.com/BeaconEthereum
Telegram: https://t.me/EthereumBeacon
ETH : 0x841195014dd6AE32F3eC4B914fbEB1CCc73aC51E

Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar